Which Best Describes the Ph of Acid Deposition
Tap card to see definition. PH 86 E.

Unit 7 Review Atmospheric Pollution Science Quizizz
Its estimated that more than 90 of the streams in this forest are acidic due to acid deposition.

. Wet deposition includes oxides of sulphur and nitrogen and acidic particles brought down as rain fog and snow. Flowing water wears away the sharp edges of river rocks. Click again to see term.
An acid is a particle or ion capable of giving a hydron proton or hydrogen ion H or alternatively able of creating a covalent bond with an electron pair a Lewis acid. PH 56 B. Others however are acid-sensitive and will be lost as the pH declines.
An acid is a material that can deliver a proton or hydrogen ion H. A A reduction in environmental lead leading to decreased negative health effects in humans and wildlife B A reduction in sulfur for crops as a result of less acidic rainfall leading to an increased need for. All of the following describe soils that are vulnerable to acid deposition except.
The soil samples are the same size and contain the same ratios of sand silt and clay. Acid deposition has harmful effects for terrestrial ecosystems when it falls below a. Acid deposition is best classified as a A.
Large volcanic eruptions have led to a decrease in the worlds photosynthetic activity because of A particulate matter which spreads in the atmosphere and scatters sunlight. The Ecological Society of America The Nations Largest Community of. Because of the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
D Water seeps into cracks in a rock freezes and melts. They design a laboratory experiment in which rainwater of different pH values is used to water soil samples taken from red spruce forests. What does acid deposition include.
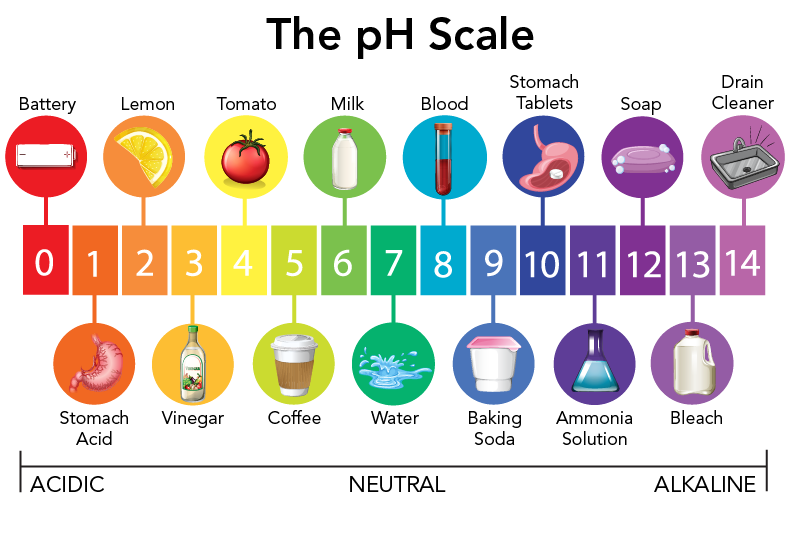
Acid deposition typically has a pH below 4 but this may be as low as 15 under seriously acidic conditions. When nitrogen or sulphur oxides dissolve in water to form HNO3 HNO2 and H2SO3. 7 pH 56 D.
Normally water has an equilibrium amount of hydrogen H and hydroxide ions OH- that are at a molar concentration of 10-7 moles per liter. PH 7 is neutral - pure water below 7 is acidic above 7 is alkaline pH is logarithmic not linear. PH strong and weak acids and acid deposition.
Tap card to see definition. Sunlight increases the rate of most of the SO 2 and NO reactions. PH strong and weak acids and acid deposition.
Click card to see definition. Hydrogen chloride in water suspension ionizes and converts to hydrogen ions and chloride ions. Rankings worst to best.
Click again to see term. Which of these is the best example of deposition. Aluminium disturbs the fishs ability to regulate the.
The result is a mild solution of sulfuric acid and nitric acid. It primarily consists of two types of compounds namely sulphuric acid H 2 SO 4 and nitric acid HNO 3. Acid rain changes the chemical composition of limestone.
Which of the following best describes a potential unintended negative consequence of implementing measures to control acid deposition. 7 pH 86. Granite Basalt Marble.
Which best describes the pH of acid deposition. The dissolved CO2 and has a pH of 56. Why is normal unpolluted rain slightly acidic.
Topics 83 84 and 85 Exploring the relative strengths of acids and bases and how we calculate pH. At lower pH levels some adult fish die. At pH 5 most fish eggs cannot hatch.
Granite and basalt barely neutralized the acid as they both lowered the pH slightly from 6 to 5. Normal precipitation has a pH of about 56 and acid deposition has a pH typically in the range of 42 to 44 according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA. A reduction in sulfur for crops as a result of less acidic rainfall leading to an increased need for sulfur supplements.
Acid rain is a broad term used to describe several ways that acids fall out of the atmosphere. Is Little Echo Pond which has a pH of 42 due to acid deposition. Also in the Northeastern US.
Scientists are interested in how the severity of acid deposition affects the soil of the red spruce forests. Generally the young of most species are more sensitive to environmental conditions than adults. The daily production of sulfur dioxide by a nearby factory ou Answered ou Answered The presence of particulate matter in the air each day 0 3 pts Question 3 0604 MC An ecologist suspects that an otherwise healthy forest ecosystem experienced an unusually high level of acid deposition during a rainy spring due to the emissions of nearby power plant.
PH of 56 caused by the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere Certain pollutants increase the acidification of rain and can fall lower than pH 2 Main primary pollutants leading to acid deposition are sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides they react with water to form strong acids sulphuric and nitric acids Sulphur dioxide is produced by. Tap again to see term. The marble neutralized the acid the best as the starting pH was about 6 and ended up at around 7 overnight.
This gives rise to a pH of 7. A more precise term is acid deposition which has two parts. From acid deposition ends up in streams and rivers.
Which of the following best describes a potential unintended negative consequence of implementing measures to control acid deposition. PH 42 which is 25 times grater than pure rain water. Dry depostion is when there is an absence of rain and precipitation.
Some types of plants and animals are able to tolerate acidic waters and moderate amounts of aluminum. C A glacier melts and drops the sediment it was carrying. How is Acid Deposition formed.
7 pH 56 C. The relative acidity of water is usually reported as the pH of the solution defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration pH -log H.

Acid Precipitation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

No comments for "Which Best Describes the Ph of Acid Deposition"
Post a Comment